A vasectomy is a highly effective surgical procedure that is performed to provide permanent contraception for men. It is a popular choice for couples who have decided that they do not want any more children.
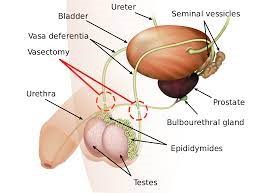
A vasectomy involves surgically cutting or blocking the tubes (vas deferens) that carry sperm from the testicles to the penis. By doing so, the man’s semen will no longer contain any sperm, making it impossible to fertilise an egg.
Before the Procedure:
Before scheduling a vasectomy, it’s important to discuss the decision with a doctor to ensure that it’s the right choice for you. The doctor will likely ask about your medical history and perform a physical exam to ensure you are a suitable candidate.
In preparation for the procedure, it’s recommended to wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing and arrange for someone to drive you home afterwards. It’s also important to avoid taking any blood-thinning medications for a few days before the procedure.
During the Procedure:
A vasectomy typically takes about 20-30 minutes and can be performed in a doctor’s office or clinic under local anaesthesia. The doctor will make one or two small incisions in the scrotum and then cut or block the vas deferens.
There are two types of vasectomy procedures:
- Traditional Vasectomy: In this procedure, the doctor will make two small incisions on either side of the scrotum to access the vas deferens. The tubes are then cut, and the ends are tied or sealed.
- No-Scalpel Vasectomy: This procedure involves making a small puncture in the scrotum instead of an incision. The doctor will then use special instruments to reach the vas deferens and block or cut them.
After the Procedure:
After the procedure, it’s normal to experience some swelling, bruising, and discomfort in the scrotum. Applying ice packs and taking over-the-counter pain medication can help alleviate these symptoms.
It’s important to avoid strenuous activities and sexual intercourse for at least a week following the procedure to allow the body time to heal.
Men should also abstain from sexual activity or use another form of contraception until their doctor confirms that their semen is free of sperm. This typically takes about 3 months and requires a follow-up semen test to make sure the semen is clear of sperm.
What are the side effects of a vasectomy?
While vasectomy is a safe and effective form of permanent birth control, as with any medical procedure, there are potential complications that can arise. It’s important for patients to be aware of these risks and discuss them with their doctor before undergoing the procedure.
- Infection: Infection is a potential complication of any surgical procedure, including vasectomy. Symptoms of infection include fever, redness, swelling, and tenderness at the incision site. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
- Bleeding or Hematoma: Bleeding or hematoma (a collection of blood outside of a blood vessel) can occur after vasectomy. Symptoms of bleeding or hematoma include swelling, bruising, and pain in the scrotum. In severe cases, surgery may be required to stop the bleeding.
- Sperm Granuloma: A sperm granuloma is a lump that forms when sperm leak from the vas deferens and causes inflammation. Symptoms of a sperm granuloma include pain and swelling in the scrotum. In some cases, surgical removal of the granuloma may be necessary.
- Vasectomy Failure: While vasectomy is considered a highly effective form of birth control, there is a small risk of failure. This can occur if the vas deferens reconnects or if sperm leaks through the blocked tubes. It’s important to use another form of birth control until a follow-up appointment confirms that the procedure was successful.
- Post-Vasectomy Pain Syndrome: Post-vasectomy pain syndrome is a condition that causes chronic pain in the scrotum after a vasectomy. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be related to nerve damage or inflammation. Treatment may include medication, physical therapy, or surgery in severe cases.
It’s important to note that these complications are rare, and most men who undergo vasectomy experience few or no complications. It’s important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with a doctor and to follow all post-operative instructions to reduce the risk of complications.
How painful is a vasectomy?
One of the concerns that many men have before undergoing vasectomy is how painful the procedure will be.
Most men experience some level of discomfort during a vasectomy, but the level of pain varies from person to person. The procedure itself is usually done under local anaesthesia, which numbs the area around the scrotum. Some men may still feel some pressure or pulling during the procedure, but they should not feel any pain.
After the procedure, men may experience some pain or discomfort in the scrotum for a few days to a week. This discomfort can range from mild to moderate and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Some men may also experience swelling or bruising in the scrotum after the procedure. Ice packs and supportive underwear can help alleviate these symptoms.
Is a vasectomy effective?
Vasectomy is considered one of the most effective forms of contraception. According to the American Urological Association, the failure rate for vasectomy is less than 1%. This means that out of 1000 couples who use vasectomy as a form of contraception, less than 1 will get pregnant in the first year after the procedure.
It is important to note that vasectomy does not provide immediate contraception. It takes a few months for all of the remaining sperm to be cleared from the man’s reproductive system. During this time, it is still possible to get pregnant. Couples who choose vasectomy as a form of contraception should use an alternative form of contraception, such as condoms until the man’s semen is confirmed to be sperm-free.
Is a vasectomy reversible?
While a vasectomy is considered to be a very effective form of contraception, some men may decide later in life that they want to have children.
A vasectomy can be reversed through a surgical procedure called vasectomy reversal. During this procedure, the tubes that were cut or blocked during the original vasectomy are reconnected, allowing sperm to once again be present in the semen.
Vasectomy reversal is not a guarantee of fertility, however. The success of the procedure depends on several factors, including the length of time since the original vasectomy, the age of the man, and the overall health of his reproductive system. Success rates for vasectomy reversal vary, but on average, about 50-70% of men will have viable sperm in their semen after the procedure.
It is also important to note that a reversal of vasectomy is more complex and invasive than the original vasectomy. It typically requires general anaesthesia and a longer recovery time.
What are the benefits of a vasectomy?
Vasectomy offers several benefits over other forms of contraception. It is a permanent form of contraception, meaning that there is no need for a man to use other forms of contraception after the procedure. It is also a very effective form of contraception with a very low failure rate.
Vasectomy is a safe and simple procedure that can be performed in a doctor’s office or clinic. It is a one-time procedure that does not require any ongoing maintenance or follow-up appointments.
Another benefit of vasectomy is that it does not affect a man’s sexual function or pleasure. The man will still be able to have an erection and orgasm, and his ejaculate will still look and feel the same. The only difference is that the semen will no longer contain sperm.
Conclusion:
Vasectomy is a safe and effective form of permanent birth control for men. It is a relatively simple procedure that can be performed in a doctor’s office or clinic under local anaesthesia. While it’s important to discuss the decision with a doctor before scheduling the procedure, vasectomy is considered a low-risk option with a high success rate.
Author: Mr Neil Haldar MBBS MD FRCS
Consultant Urological Surgeon
The Pelvic Specialists
